Getting Started¶
Overview¶
This section provides a step-by-step guide to setting up the Arduino IDE and preparing your ESP32 D1 Mini (WROOM-32) for uploading the evolutronix state machine firmware. All software tools used here are free and can be installed on Windows, macOS, or Linux.
Arduino IDE Installation¶
To upload firmware to the ESP32 board, we use the Arduino IDE. Download the installer from the official Arduino website:
🔗 https://www.arduino.cc/en/software
After downloading, follow the installation wizard for your operating system. Once installed, open the Arduino IDE to verify that it runs correctly.
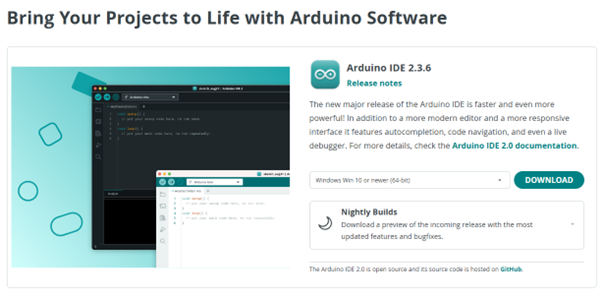
Fig. 7 Figure 1 – Download page of the Arduino IDE.¶
Setting up the ESP32 Board¶
After the Arduino IDE is installed, you need to install the ESP32 board definitions to enable support for your hardware.
Open the Arduino IDE.
Navigate to File → Preferences.
Copy and paste the following URL into the “Additional Boards Manager URLs” field:
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json
or
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/gh-pages/package_esp32_index.json
Click OK, then open Tools → Board → Boards Manager.
Search for ESP32 by Espressif Systems and install the latest version (for example: version 3.x).
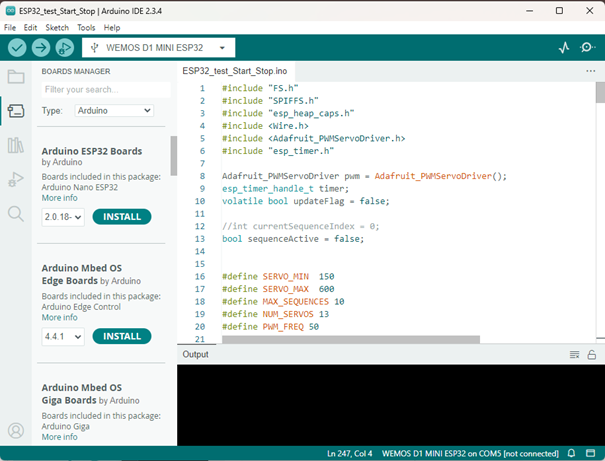
Fig. 8 Figure 2 – Installing the ESP32 board in the Arduino IDE.¶
Installing USB-to-UART Drivers¶
Your computer requires the correct USB driver to communicate with the ESP32.
For the ESP32-WROOM-32, download and install the CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Driver from Silicon Labs:
🔗 https://www.silabs.com/developers/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers?tab=downloads
Select the appropriate driver version for your operating system.
Note
Some ESP32 variants may use CH340 drivers instead of CP210x. If your device is not detected after installation, install the CH340 driver and reconnect your board.
Testing the ESP32 Installation¶
Now that all software and drivers are installed, you can verify the setup by uploading a simple LED blink example.
Step 1: Open the Arduino IDE and go to File → New. Copy the following code into the editor:
1#include <Arduino.h>
2
3#define LED 2
4
5void setup() {
6 Serial.begin(115200);
7 pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
8}
9
10void loop() {
11 digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
12 Serial.println("LED is on");
13 delay(1000);
14 digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
15 Serial.println("LED is off");
16 delay(1000);
17}
Step 2: Select your board and port:
Navigate to Tools → Board → Select other board and port…
Choose your ESP32 model (for example: DOIT ESP32 DEVKIT V1).
Select the correct COM port, then click OK.
Step 3: Click the Upload button. If prompted, hold the BOOT button on your ESP32 board while the code is uploading.

Fig. 9 Figure 4 – Uploading the blink example.¶
Once the upload completes successfully, the on-board LED (GPIO 2) should blink every second, confirming that your ESP32 and Arduino IDE are working correctly.
Summary¶
You have now:
Installed the Arduino IDE
Configured the ESP32 board manager
Installed the required USB-to-UART drivers
Uploaded and verified your first program
esp32 state machine¶
copy de tekst and past in arduino and save upload to esp32
1 #include "FS.h"
2 #include "SPIFFS.h"
3 #include "esp_heap_caps.h"
4 #include <Wire.h>
5 #include <Adafruit_PWMServoDriver.h>
6 #include "esp_timer.h"
7
8 Adafruit_PWMServoDriver pwm = Adafruit_PWMServoDriver();
9 esp_timer_handle_t timer;
10 volatile bool updateFlag = false;
11
12 //int currentSequenceIndex = 0;
13 bool sequenceActive = false;
14
15
16 #define SERVO_MIN 150
17 #define SERVO_MAX 600
18 #define MAX_SEQUENCES 10
19 #define NUM_SERVOS 13
20 #define PWM_FREQ 50
21
22 struct Sequence {
23 int angle[NUM_SERVOS];
24 int speed[NUM_SERVOS];
25 };
26
27 struct Group {
28 String name;
29 Sequence sequences[MAX_SEQUENCES];
30 int numSequences;
31 };
32
33 struct ServoControl {
34 uint8_t channel;
35 int currentAngle = 90;
36 int targetAngle = 90;
37 int speedDelay = 20;
38 unsigned long lastUpdate = 0;
39 ServoControl(uint8_t ch) : channel(ch) {}
40 };
41
42 ServoControl servos[NUM_SERVOS] = {
43 {0}, {1}, {2}, {3}, {4}, {5}, {6}, {7}, {8}, {9}, {10}, {11}, {12}
44 };
45
46 bool reachedTarget[NUM_SERVOS] = {false};
47
48 // Forward declarations
49 void saveSequenceToFile(String input);
50 void MoveServo(String input);
51 void loadSequenceGroupFromFile(const String& fileName);
52 void loadSequenceGroupFromSerial(const String& serialData);
53 void parseSequenceGroupData(const String& groupName, const String& rawData);
54 int angleToPWM(int angle);
55 void printFreeHeap();
56 void printMemoryInfo();
57 void IRAM_ATTR onTimer(void* arg);
58 void moveServoTo(int index, int angle);
59
60
61 Group currentGroup;
62
63 String input;
64 bool isPlaying = false;
65 bool loopSequences = false;
66 float globalSpeedFactor = 1.0f;
67 int currentSequenceIndex = 0;
68
69
70
71 class CommandHandler {
72 public:
73 void processCommand(String input) {
74 if (input.length() < 3) return;
75 input = input.substring(1, input.length() - 1);
76 int firstComma = input.indexOf(',');
77 String mainCommand = (firstComma != -1) ? input.substring(0, firstComma) : input;
78 String parameters = (firstComma != -1) ? input.substring(firstComma + 1) : "";
79
80 if (mainCommand == "PLAY") {
81 loadSequenceGroupFromFile(parameters);
82 currentSequenceIndex = 0;
83 isPlaying = true;
84 } else if (mainCommand == "SAVE") {
85 saveSequenceToFile(parameters);
86 } else if (mainCommand == "RUN") {
87 loadSequenceGroupFromSerial(parameters);
88 currentSequenceIndex = 0;
89 isPlaying = true;
90 } else if (mainCommand == "MOVE") {
91 MoveServo(parameters);
92 } else if (mainCommand == "STOP") {
93 isPlaying = false;
94 } else if (mainCommand == "START") {
95 isPlaying = true;
96 } else if (mainCommand == "LOOP") {
97 loopSequences = (parameters.toInt() == 1);
98 } else if (mainCommand == "SPEED") {
99 globalSpeedFactor = parameters.toFloat();
100 if (globalSpeedFactor <= 0.0f) globalSpeedFactor = 1.0f;
101 } else {
102 Serial.println("Onbekend commando!");
103 }
104 }
105 };
106
107 void IRAM_ATTR onTimer(void* arg) {
108 updateFlag = true;
109 }
110
111 // Globalen
112
113 CommandHandler handler;
114
115
116 void setup() {
117 Serial.begin(115200);
118 pwm.begin();
119 pwm.setPWMFreq(PWM_FREQ);
120 if (!SPIFFS.begin(true)) {
121 Serial.println("SPIFFS mount failed");
122 return;
123 }
124 const esp_timer_create_args_t timer_args = {
125 .callback = &onTimer,
126 .arg = nullptr,
127 .dispatch_method = ESP_TIMER_TASK,
128 .name = "servo_update_timer"
129 };
130 esp_timer_create(&timer_args, &timer);
131 esp_timer_start_periodic(timer, 1000); // elke 1 ms
132 }
133
134 void loop() {
135 while (Serial.available()) {
136 char received = Serial.read();
137 if (received == '>') {
138 input += received;
139 handler.processCommand(input);
140 input = "";
141 } else if (received == '<') {
142 input = "<";
143 } else {
144 input += received;
145 }
146 }
147
148 if (updateFlag) {
149 updateFlag = false;
150 if (!isPlaying || currentGroup.numSequences == 0) return;
151
152 Sequence& seq = currentGroup.sequences[currentSequenceIndex];
153 bool allReached = true;
154
155 for (int i = 0; i < NUM_SERVOS; i++) {
156 int delta = seq.angle[i] - servos[i].currentAngle;
157 if (abs(delta) > 0) {
158 int dir = (delta > 0) ? 1 : -1;
159 int stepSize = max(1, (int)(seq.speed[i] * globalSpeedFactor));
160 servos[i].currentAngle += dir * min(abs(delta), stepSize);
161 moveServoTo(i, servos[i].currentAngle);
162 allReached = false;
163 }
164 }
165
166 if (allReached) {
167 currentSequenceIndex++;
168 if (currentSequenceIndex >= currentGroup.numSequences) {
169 if (loopSequences) currentSequenceIndex = 0;
170 else isPlaying = false;
171 }
172 }
173 }
174 }
175
176 int angleToPWM(int angle) {
177 return map(angle, 0, 180, 102, 512);
178 }
179
180 void moveServoTo(int index, int angle) {
181 int pulse = angleToPWM(angle);
182 pwm.setPWM(servos[index].channel, 0, pulse);
183 }
184
185 void MoveServo(String parameters) {
186 int commaIndex = parameters.indexOf(',');
187 if (commaIndex == -1) return;
188 int servoId = parameters.substring(0, commaIndex).toInt();
189 int position = parameters.substring(commaIndex + 1).toInt();
190 if (servoId >= 0 && servoId < NUM_SERVOS) {
191 moveServoTo(servoId, position);
192 servos[servoId].currentAngle = position;
193 }
194 }
195
196 void saveSequenceToFile(String input) {
197 int firstComma = input.indexOf(',');
198 if (firstComma == -1) return;
199 String fileName = input.substring(0, firstComma);
200 String data = input.substring(firstComma + 1);
201 File file = SPIFFS.open("/" + fileName + ".txt", FILE_WRITE);
202 if (!file) return;
203 file.println(data);
204 file.close();
205 }
206
207 void loadSequenceGroupFromFile(const String& fileName) {
208 File file = SPIFFS.open("/" + fileName + ".txt", FILE_READ);
209 if (!file) return;
210 String content = file.readString();
211 file.close();
212 parseSequenceGroupData(fileName, content);
213 }
214
215 void loadSequenceGroupFromSerial(const String& serialData) {
216 int firstComma = serialData.indexOf(',');
217 if (firstComma == -1) return;
218 String groupName = serialData.substring(0, firstComma);
219 String dataPart = serialData.substring(firstComma + 1);
220 parseSequenceGroupData(groupName, dataPart);
221 }
222
223 void parseSequenceGroupData(const String& groupName, const String& rawData) {
224 currentGroup.name = groupName;
225 currentGroup.numSequences = 0;
226 String content = rawData;
227 content.trim();
228 int pos = 0;
229 while ((pos = content.indexOf("sequence", pos)) != -1 && currentGroup.numSequences < MAX_SEQUENCES) {
230 int next = content.indexOf("sequence", pos + 1);
231 String seqData = (next != -1) ? content.substring(pos, next) : content.substring(pos);
232 Sequence& seq = currentGroup.sequences[currentGroup.numSequences];
233 memset(&seq, 0, sizeof(Sequence));
234 int dataStart = seqData.indexOf(',') + 1;
235 seqData = seqData.substring(dataStart);
236 for (int i = 0; i < NUM_SERVOS && seqData.length() > 0; i++) {
237 int comma1 = seqData.indexOf(',');
238 if (comma1 == -1) break;
239 seq.angle[i] = seqData.substring(0, comma1).toInt();
240 seqData = seqData.substring(comma1 + 1);
241 int comma2 = seqData.indexOf(',');
242 seq.speed[i] = (comma2 == -1) ? seqData.toInt() : seqData.substring(0, comma2).toInt();
243 seqData = (comma2 == -1) ? "" : seqData.substring(comma2 + 1);
244 }
245 currentGroup.numSequences++;
246 pos = next;
247 }
248 }
Evolutronix GUI¶
Nu hebben we nog de evolutronix GUI nodig download de evolutronix GUI vanaf hun website www.evolutronix-robotics.com
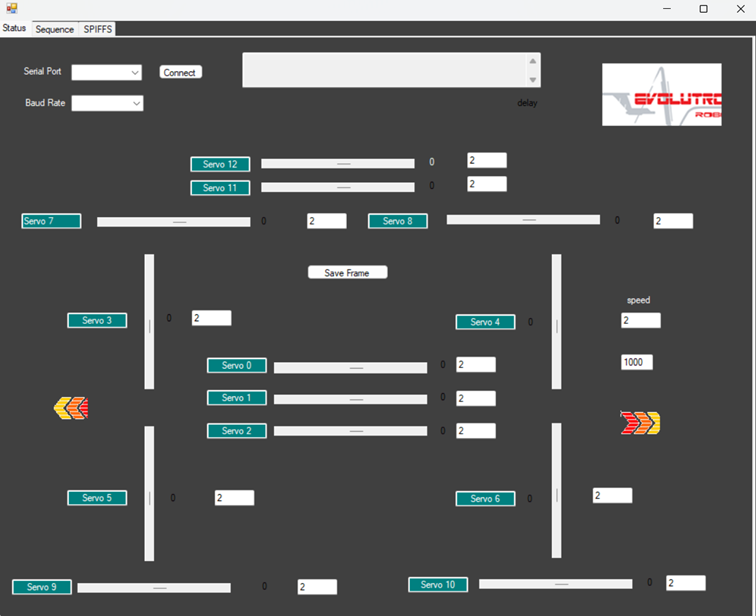
Fig. 10 Figure 4 – Evolutronix GUI.¶
In the next section, we will move on to configuring the electronics setup and connecting the servo controller.